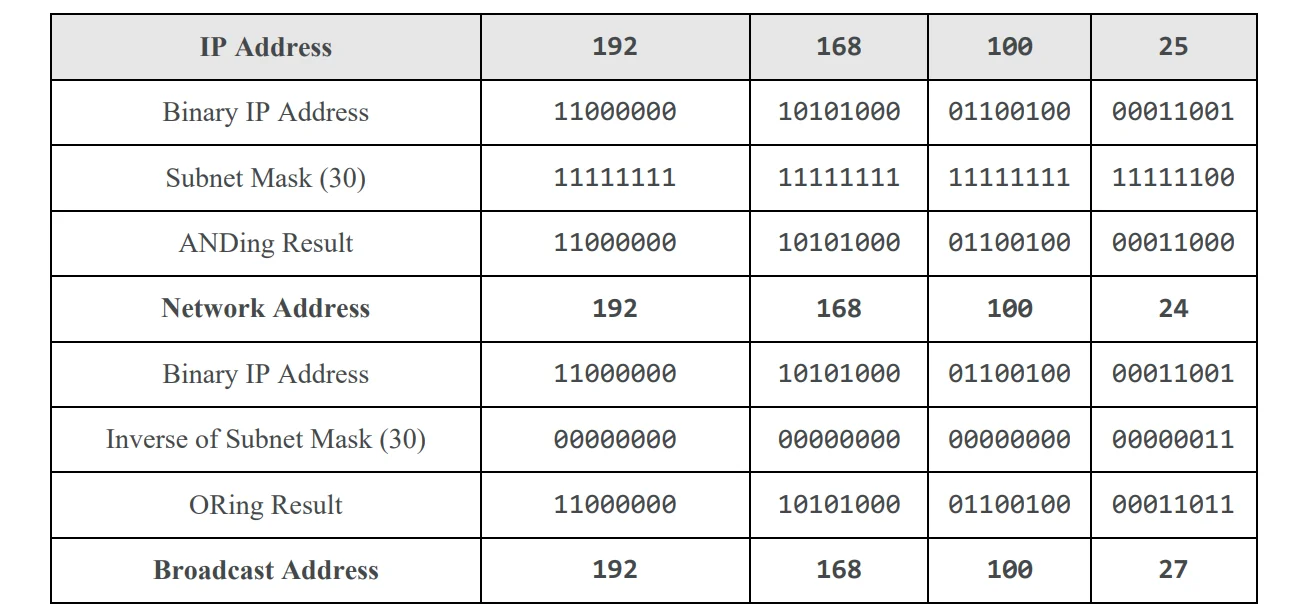
Subnetting
Subnetting is defined as breaking down of huge network address to manageable networks. For the subnet addressing scheme to work, every host on the network must know which part of the host address will be used as the subnet address. The table gives the default subnet mask of each class.
CIDR notation indicates the network mask for an address and adds on the total number of turned on bits in the entire address using slash notation.
Default Subnet Mask
| Class | Format | Default Subnet Mask | CIDR |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | network.host.host.host | 255.0.0.0 | /8 |
| B | network.network.host.host | 255.255.0.0 | /16 |
| C | network.network.network.host | 255.255.255.0 | /24 |
Subnetting Formula
How many subnets? 2x = number of subnets. x is the number of masked bits or turned on network bit.
How many hosts per subnet? 2y – 2 = number of hosts per subnet. y is the number of unmasked bits or turned off host bit.
What are the valid subnets? 256 – subnet mask = block size
What’s the broadcast address for each subnet? The number right before the value of the next subnet.
| Subnet | 0 | 128 |
|---|---|---|
| First host | 1 | 129 |
| Last host | 126 | 254 |
| Broadcast Address | 127 | 255 |
Real-world Problem
Scenario I
192.168.1.0/24 network address is assigned to do subnetting for the topology seen below.
Explanation I
Total required networks include:
- 2 LANs individually connected with the highest number of connected hosts, that is 2.
- 1 WAN between routers
- Given network address is 192.168.1.0/24 which belongs to Class C with default subnet mask 255.255.255.0
- If we subnet with /26 i.e., 255.255.255.192, then block size is: 256 – 192 = 64
- Subnetwork: 22 = 4
- Valid Hosts per subnetwork 26 - 2 = 62
Answer I
- How many subnetworks can be seen as requirements in the figure above? 3
- How many maximum hosts are required in any subnetwork? 3
- How many bits will be borrowed from hosts portion in order to accommodate the required number of subnets? 2
- How many subnetworks will be created by borrowing the bits as mentioned above? 22 = 4
- How many subnetworks will remain unused for future use? 4 – 3 = 1
- How many valid host addresses will be available per subnetwork? 26 - 2 = 62
- After changing the length/CIDR of original network, what is the new subnet mask? 255.255.255.192
- Fill in the following table with the subnetwork’s information.
| Subnetwork # | Subnetwork Address | First Valid Host | Last Valid Host | Broadcast Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 192.168.1.0 | 192.168.1.1 | 192.168.1.62 | 192.168.1.63 |
| 2 | 192.168.1.64 | 192.168.1.65 | 192.168.1.126 | 192.168.1.127 |
| 3 | 192.168.1.128 | 192.168.1.129 | 192.168.1.190 | 192.168.1.191 |
| 4 | 192.168.1.192 | 192.168.1.193 | 192.168.1.254 | 192.168.1.255 |
Scenario II
192.168.20.0/24 network address is assigned to you to do subnetting for the topology seen below.
Explanation II
Total required networks include:
- 4 LANs individually connected with the highest number of connected hosts, that is 3.
- 4 WAN between routers
- Given network address is 192.168.20.0/24 which belongs to Class C with default subnet mask 255.255.255.0
- If we subnet with /27 i.e., 255.255.255.224, then block size: 256 – 192 = 64
- Subnetwork: 23 = 8
- Valid Hosts per subnetwork 25 - 2 = 30
Answer II
- How many subnetworks can be seen as requirements in the figure seen above? 8
- How many maximum hosts are required in any subnetwork? 3
- How many bits will be borrowed from hosts portion in order to accommodate the required number of subnets? 3
- How many subnetworks will be created by borrowing the bits as mentioned above? 23 = 8
- How many subnetworks will remain unused for future use? 8 – 8 = 0
- How many valid host addresses will be available per subnetwork? 25 - 2 = 30
- After changing the length/CIDR of original network, what is the new subnet mask? 255.255.255.224
- Fill in the following table with the subnetwork’s information.
| Subnetwork # | Subnetwork Address | First Valid Host | Last Valid Host | Broadcast Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 192.168.20.0 | 192.168.20.1 | 192.168.20.30 | 192.168.20.31 |
| 2 | 192.168.20.32 | 192.168.20.33 | 192.168.20.62 | 192.168.20.63 |
| 3 | 192.168.20.64 | 192.168.20.65 | 192.168.20.94 | 192.168.20.95 |
| 4 | 192.168.20.96 | 192.168.20.97 | 192.168.20.126 | 192.168.20.127 |
| 5 | 192.168.20.128 | 192.168.20.129 | 192.168.20.158 | 192.168.20.159 |
| 6 | 192.168.20.160 | 192.168.20.161 | 192.168.20.190 | 192.168.20.191 |
| 7 | 192.168.20.192 | 192.168.20.193 | 192.168.20.222 | 192.168.20.223 |
| 8 | 192.168.20.224 | 192.168.20.225 | 192.168.20.254 | 192.168.20.255 |
Scenario III
172.16.0.0/16 network address is assigned to you to do subnetting for the topology seen below.
Explanation III
Total required networks include:
- 9 LANs individually connected with the highest number of connected hosts, that is 3900.
- 6 WANs between routers. 4
- Given network address is 172.16.0.0/16 which belongs to Class B with default subnet mask 255.255.0.0
- If we subnet with /20 i.e., 255.255.240.0, then the block size: 256 – 240 = 16
- Subnetwork: 24 = 16
- Valid hosts per subnetwork 212 - 2 = 4094
Answer III
- How many subnetworks can be seen as requirements in the figure seen above? 15
- How many maximum hosts are required in any subnetwork? 3900
- How many bits will be borrowed from the host portion in order to accommodate the required number of subnets? 4
- How many subnetworks will be created by borrowing the bits as mentioned above? 24 = 16
- How many subnetworks will remain unused for future use? 16 – 15 = 1
- How many valid host addresses will be available per subnetwork? 212 - 2 = 4094
- After changing the length/CIDR of original network, what is the new subnet mask? 255.255.240.0
- Fill in the following table with the subnetwork’s information.
| Subnetwork # | Subnetwork Address | First Valid Host | Last Valid Host | Broadcast Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 172.16.0.0 | 172.16.0.1 | 172.16.15.254 | 172.16.15.255 |
| 2 | 172.16.16.0 | 172.16.16.1 | 172.16.31.254 | 172.16.31.255 |
| 3 | 172.16.32.0 | 172.16.32.1 | 172.16.47.254 | 172.16.47.255 |
| 4 | 172.16.48.0 | 172.16.48.1 | 172.16.63.254 | 172.16.63.255 |
| 5 | 172.16.64.0 | 172.16.64.1 | 172.16.79.254 | 172.16.79.255 |
| 6 | 172.16.80.0 | 172.16.80.1 | 172.16.95.254 | 172.16.95.255 |
| 7 | 172.16.96.0 | 172.16.96.1 | 172.16.111.254 | 172.16.111.255 |
| 8 | 172.16.112.0 | 172.16.112.1 | 172.16.127.254 | 172.16.127.255 |
| 9 | 172.16.128.0 | 172.16.128.1 | 172.16.143.254 | 172.16.143.255 |
| 10 | 172.16.144.0 | 172.16.144.1 | 172.16.159.254 | 172.16.159.255 |
| 11 | 172.16.160.0 | 172.16.160.1 | 172.16.175.254 | 172.16.175.255 |
| 12 | 172.16.176.0 | 172.16.176.1 | 172.16.191.254 | 172.16.191.255 |
| 13 | 172.16.192.0 | 172.16.192.1 | 172.16.207.254 | 172.16.207.255 |
| 14 | 172.16.208.0 | 172.16.208.1 | 172.16.223.254 | 172.16.223.255 |
| 15 | 172.16.224.0 | 172.16.224.1 | 172.16.239.254 | 172.16.239.255 |
| 16 | 172.16.240.0 | 172.16.240.1 | 172.16.255.254 | 172.16.255.255 |